Thermography

Detection of temperature changes
Analysis of structural problems
Environmental monitoring
Thermography captures and analyses thermal information without direct contact, recording infrared radiation and converting it into visible images. It is divided into two stages: thermographic survey and analysis. In surveying, drones with thermal imaging cameras observe and acquire thermal images, converting heat into electrical pulses visible as thermograms. The analysis uses software to process data, measure surface temperatures, and create false-colour maps that highlight thermal anomalies. The emissivity of objects varies: those with low emissivity reflect temperatures similar to surrounding objects, while those with high emissivity provide more accurate readings.
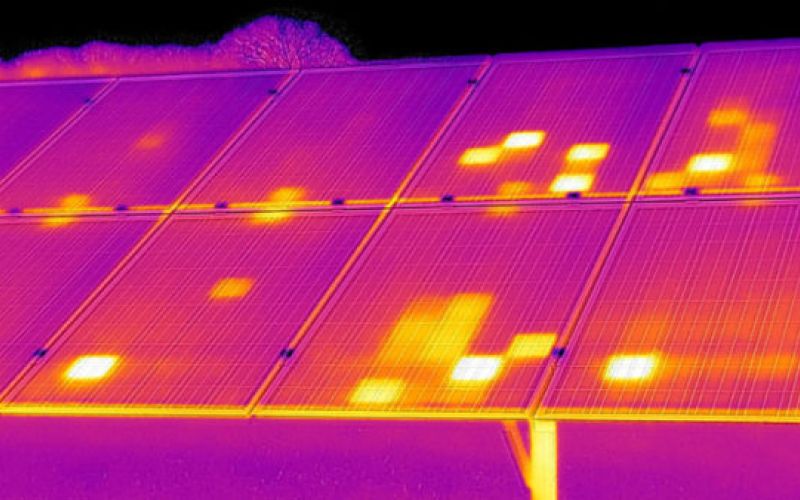


The use of drones in thermography offers great versatility and finds application in various contexts. In construction, drones detect thermal bridges, defects in coats, moisture and mould through infrared monitoring, preventing costly future maintenance. In industry, drones provide data on the condition of electrical, chemical and mechanical elements. For photovoltaic panels, thermographic inspections quickly detect “hot spots” caused by damaged cells, allowing targeted interventions without altering the structure. Thermal imaging taken by drones is essential to identify problems efficiently and noninvasively.